Introduction: Java Cache
From Resin 4.0 Wiki
| Line 60: | Line 60: | ||
== 20% miss, 100ms miss time, 1ms hit time == | == 20% miss, 100ms miss time, 1ms hit time == | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Cache-20-miss-changes.png]] | ||
<table border="1"> | <table border="1"> | ||
Revision as of 00:00, 29 January 2012
Faster application performance is possible with Java caching by saving the results of long calculations and reducing database load. The Java caching API is being standardized with jcache. In combination with Java Dependency Injection (CDI), you can use caching in a completely standard fashion in the Resin Application Server. You'll typically want to look at caching when your application starts slowing down, or your database or other expensive resource starts getting overloaded. Caching is useful when you want to:
- Improve latency
- Reduce database load
- Reduce CPU use
Contents |
Cache Performance Benefits
Since reducing database load is a typical cache benefit, it's useful to create a micro-benchmark to see how a cache can help. This is just a simple test with mysql running on the same server and a trivial query. In other words, it's not trying to exaggerate the value of the cache, because almost any real cache use will have a longer "doLongCalculation" than this simple example, and therefore the cache will benefit even more.
The micro-benchmark has a simple jdbc query in the "doLongCalculation" method
"SELECT value FROM test WHERE id=?"
and then to get useful data, the call to "doStuff" is repeated 300k times and compared with the direct call to "doLongCalculation" 300k times.
| Type | Time | requests per millisecond | Mysql CPU |
|---|---|---|---|
| JDBC | 30s | 10.0 req/ms | 35% |
| Cache | 0.3s | 1095 req/ms | 0% |
Even this simple test shows how caches can win. In this simple benchmark, the performance is significantly faster and saves the database load.
- 10x faster
- Remove Mysql load
To get more realistic numbers, you'll need to benchmark the difference on a full application. Micro-benchmarks like this are useful to explain concepts, but real benchmarks require testing against your own application, in combination with profiling. For example, Resin's simple profiling capabilities in the /resin-admin or with the pdf-report can get you quick and simple data in your application performance.
The Resin ClusterCache implementation
Since Resin's ClusterCache is a persistent cache, the entries you save will be stored to disk and recovered. This means you can store lots of data in the cache without worrying about running out of memory. (LocalCache is also a persistent cache.) If the memory becomes full, Resin will use the cache entries that are on disk. For performance, commonly-used items will remain in memory.
Cache Performance
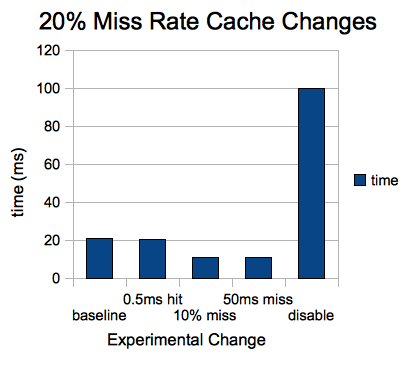
t = p_miss * t_miss + (1 - p_miss) * t_hit
20% miss, 100ms miss time, 1ms hit time
| Change | Performance |
|---|---|
| no change | 20.8ms |
| 0.5ms hit time | 20.4ms |
| 10% miss rate | 10.9ms |
| 50ms miss time | 10.8ms |
| disable cache | 100ms |